HSE Needle Exchange Programme Insights Report
Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme – Review of Performance Indicators, Drug Insights Report 4

The HSE National Social Inclusion Office (NSIO) has launched the fourth instalment of their Drug Insights Report Series – ‘Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme – Review of Performance Indicators.’
The aim of the review is to provide an overview of patterns of use of the HSE Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme. KPI data for the HSE Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme from 2015-2022 was obtained from the HSE Planning and Business Information Unit to carry out the review.
 The HSE Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme is an important element in the Health Service Executives (HSE) implementation of a harm reduction approach, which is advocated by the National Drug and Alcohol Strategy ‘Reducing Harm, Supporting Recovery: A health-led response to drug and alcohol use in Ireland'. The increased provision of sterile needle exchange packs is central to minimizing, ‘the harms caused by the use and misuse of substances and promote rehabilitation and recovery.’.
The HSE Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme is an important element in the Health Service Executives (HSE) implementation of a harm reduction approach, which is advocated by the National Drug and Alcohol Strategy ‘Reducing Harm, Supporting Recovery: A health-led response to drug and alcohol use in Ireland'. The increased provision of sterile needle exchange packs is central to minimizing, ‘the harms caused by the use and misuse of substances and promote rehabilitation and recovery.’.
Needle exchange services provide access to sterile injecting equipment to people who inject drugs (PWID), promote safe disposal of used equipment, and facilitate access to other health services.They are a harm reduction measure that aims to reduce the impact of sharing used injecting equipment and reduce the risk of infection from discarded needles. These services were first established in Ireland in 1989 in areas that experienced high levels of substance use. The HSE Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme was introduced in 2011 to extend coverage to other areas of the country. This study aims to provide an overview of the performance of the HSE Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme.
Key performance Indicators (KPIs) for the HSE Pharmacy Needle Exchange Programme were obtained from the HSE Planning and Business Information Unit. Yearly totals for each KPI were calculated to show patterns from 2015-2022 with five-year forecasts.
You can access the report here
Overall Findings
Pharmacies - The number of pharmacies providing the programme has reduced by 18% since 2015 with 90 pharmacies enrolled in 2022. KPIs have not been met for every year except 2019. It is forecast that by 2027, the number of pharmacies will decline by a further 25%
People - There has been a 7% decline in the number of people using the programme since 2015. In 2022, 1,612 people used the programme per month (17.9 per pharmacy). KPI patterns have fluctuated but in 2022 were 7% above target (1500 people), which is forecast to stabilise with an increase of 1% by 2027.
Packs - In 2022, 3,775 packs were provided per month. There has been a 19% decline in the number of packs provided per month and a 42% decline in the number of packs returned since 2015. KPI targets have not been met with the proportion of packs returned declining from 23% in 2015 to 16% in 2022.
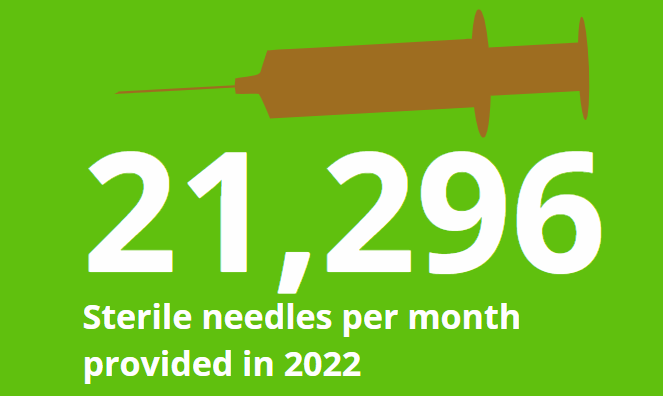
Needles - In 2022, 21,296 sterile needles per month were provided by the programme, which is a decline of 16% since 2017. There has been a 4.2 percentage point reduction in the average number of needles per individual since 2017. KPI targets for sterile needles have not been met for half of the years included in the analysis.
Future Directions 
- Receive feedback from pharmacies and people who inject drugs
- Review KPIs on a regular basis
- Ensure the scheme is compatible with current drug trends













